Introduction to Bitcoin Mining and Energy Use
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network, utilizing high-performance computing to validate transactions and secure the blockchain. However, its energy-intensive nature has drawn criticism globally. Understanding the mechanisms behind Bitcoin mining is essential to evaluate its actual environmental impact. Mining requires computational power, which in turn consumes electricity. This energy demand has sparked debates about sustainability, with both critics and proponents providing data to support their claims. Furthermore, advancements in renewable energy and energy-efficient hardware play a critical role in shaping the future of Bitcoin mining.
The Scale of Bitcoin Mining’s Energy Consumption
One of the most cited statistics about Bitcoin is its annual electricity consumption. According to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Bitcoin uses as much energy as some small nations. While this may seem alarming, it’s crucial to contextualize these numbers. Bitcoin’s energy consumption is often compared to traditional financial systems or gold mining. Additionally, per-transaction energy use can be misleading, as Bitcoin processes high-value transactions that traditional systems might split among multiple methods. Improved transparency in energy reporting can help dispel exaggerated claims.
Renewable Energy in Bitcoin Mining
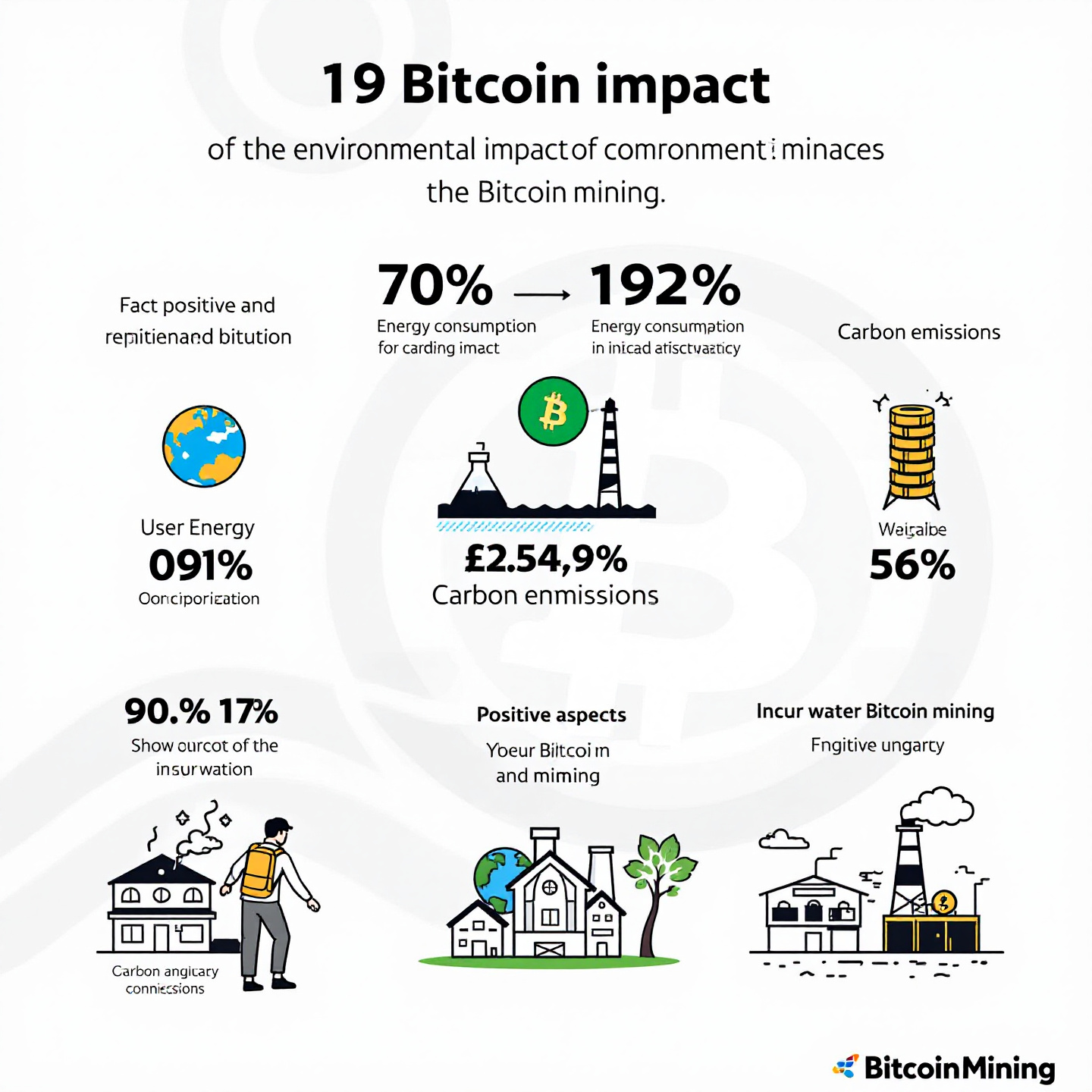
A significant portion of Bitcoin mining operations utilizes renewable energy sources. Studies indicate that up to 56% of Bitcoin’s energy consumption is derived from renewables like hydro, solar, and wind. This shift is primarily driven by the economic benefits of low-cost renewable energy in regions with surplus production. For instance, mining hubs in Iceland and Canada capitalize on geothermal and hydroelectric power, reducing their carbon footprint. By fostering partnerships with renewable energy providers, miners can further enhance sustainability while driving innovation in energy storage solutions.
Geographical Distribution of Mining Operations
Bitcoin mining is geographically concentrated in regions with cheap electricity. Previously dominated by China, mining activities have diversified to countries like the United States, Kazakhstan, and Russia. The migration has implications for environmental impact, as the energy mix varies significantly across these regions. Countries reliant on coal-heavy grids contribute more to emissions, while those leveraging renewables offer a greener alternative. This geographical shift underscores the need for global policies to promote green energy adoption in mining operations.
Common Misconceptions About Bitcoin Mining
A frequent misconception is that Bitcoin mining directly depletes energy resources, causing blackouts and energy shortages. In reality, mining often occurs in areas with abundant or stranded energy—electricity that would otherwise go unused. For example, in Texas, miners stabilize the grid by consuming surplus energy during off-peak hours and shutting down during demand spikes. By integrating demand-response systems, Bitcoin miners can play a constructive role in grid management, dispelling the myth of their detrimental energy impact.
Carbon Footprint of Bitcoin Mining
Critics often highlight the carbon emissions associated with Bitcoin mining. While mining does contribute to CO2 emissions, its overall impact remains smaller compared to industries like aviation or traditional banking. Furthermore, advancements in carbon offset programs and the adoption of cleaner energy sources are helping to mitigate these emissions. Recent partnerships between mining firms and carbon credit initiatives illustrate a proactive approach toward achieving carbon neutrality.
Energy Efficiency Innovations in Mining Technology
The Bitcoin mining industry is actively innovating to improve energy efficiency. New-generation mining hardware like ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) consumes less power per hash, making mining more sustainable. Additionally, practices like immersion cooling and heat recycling contribute to reducing environmental impact by enhancing efficiency. Mining firms that adopt these technologies not only reduce costs but also position themselves as leaders in sustainable practices.
Bitcoin Mining and Economic Development
In some regions, Bitcoin mining drives economic growth by utilizing underused energy resources and creating jobs. For instance, in rural areas with excess hydroelectric power, mining provides a revenue stream for local governments. It also incentivizes investment in renewable energy infrastructure, benefiting communities long-term. Additionally, the economic diversification brought by mining can stabilize local economies reliant on traditional industries.
Comparing Bitcoin to Traditional Financial Systems
When assessing Bitcoin’s environmental impact, it’s crucial to compare it to traditional systems. Data centers, bank branches, and ATMs collectively consume vast amounts of energy. Bitcoin offers a decentralized alternative that eliminates many of these energy-intensive infrastructures, potentially reducing overall energy demand in the financial sector. Comparative analyses reveal that Bitcoin’s decentralized model has the potential to streamline financial transactions while lowering environmental costs.
Policy and Regulatory Challenges
Governments worldwide are grappling with the environmental implications of Bitcoin mining. Some have implemented bans or restrictions, while others promote renewable integration. Policies encouraging the use of green energy for mining could address environmental concerns without stifling innovation. Clear regulations can also guide miners toward sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts between regulators and industry stakeholders are vital to achieving balanced solutions.
Solutions for a Sustainable Future in Bitcoin Mining
The path to sustainable Bitcoin mining involves collaboration between industry stakeholders, governments, and energy providers. Encouraging miners to locate in renewable-rich areas and adopt energy-efficient technologies can drastically reduce their environmental footprint. Public awareness campaigns can also dispel misconceptions and foster support for sustainable mining practices. Additionally, fostering innovation in decentralized energy grids may pave the way for more sustainable mining operations globally.
Conclusion: Facts vs. Misconceptions
Bitcoin mining’s environmental impact is a complex issue often clouded by misconceptions. While the industry faces legitimate challenges, it is also evolving to address sustainability concerns. Through innovations in energy efficiency and the growing use of renewables, Bitcoin mining is working toward a greener future. Educating the public on these developments is crucial for fostering informed debates and shaping effective policies. By balancing innovation with environmental responsibility, Bitcoin mining can align with global sustainability goals.